The Role of Probiotics in Gut Health and Immunity
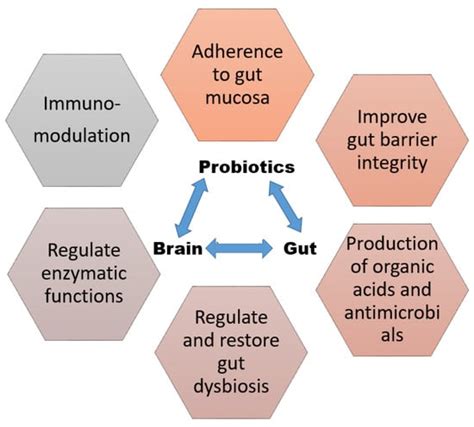
In recent years, probiotics have gained significant attention as a key component of a healthy diet and lifestyle. Often touted as "good bacteria," these microorganisms have been shown to have a positive impact on gut health, digestion, and even the immune system. But what exactly are probiotics, and how do they contribute to overall health?
In this article, we'll explore the role of probiotics in maintaining gut health and their potential influence on immune function. We’ll also discuss the scientific evidence behind these claims and how you can incorporate probiotics into your daily routine.
What Are Probiotics?
Probiotics are live microorganisms—primarily bacteria and yeast—that, when consumed in adequate amounts, confer health benefits to the host (i.e., the human body). These beneficial microbes are naturally found in the human gut, but they can also be introduced through foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and other fermented products. Probiotics can also be taken as dietary supplements in the form of capsules, tablets, powders, and liquids.
The most common types of probiotics include Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium species, as well as Saccharomyces boulardii, a type of yeast. Each type of probiotic strain offers unique benefits, and researchers are continually studying the specific roles that different strains play in human health.
Probiotics and Gut Health: The Microbiome Connection
The human gut is home to a diverse and complex ecosystem of microorganisms, collectively known as the microbiome. This microbiome includes billions of bacteria, fungi, viruses, and other microbes, which play essential roles in digestion, metabolism, and immune function. When the balance of these microorganisms is disrupted—due to factors like poor diet, stress, illness, or the use of antibiotics—the gut can become less efficient, leading to various digestive issues and health problems.
Probiotics help restore and maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria, which can improve digestion and overall gut function. Here are a few ways that probiotics support gut health:
Improved Digestion
Probiotics aid in the breakdown of food and absorption of nutrients. Certain strains of probiotics, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, produce enzymes that help break down complex carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, making it easier for the body to absorb essential nutrients.
By promoting healthy digestion, probiotics can reduce symptoms of indigestion, bloating, and constipation. Some evidence also suggests that they can help alleviate symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, and constipation.
Restoring Gut Flora After Antibiotic Use
Antibiotics are effective in treating bacterial infections, but they often disrupt the balance of gut bacteria, killing both harmful and beneficial bacteria. This disruption can lead to digestive discomfort, as well as an increased risk of infections, such as Clostridium difficile (C. diff) colitis.
Probiotics can help restore the balance of gut bacteria following antibiotic treatment, reducing the likelihood of gastrointestinal side effects and infections. Some studies suggest that taking probiotics alongside antibiotics may reduce the incidence of antibiotic-associated diarrhea.
Preventing and Treating Diarrhea
Probiotics have been shown to be effective in preventing and treating various types of diarrhea. In particular, Saccharomyces boulardii and Lactobacillus strains have been found to reduce the duration and severity of infectious diarrhea, as well as diarrhea associated with antibiotics.
Probiotics may work by promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, enhancing the gut lining’s ability to resist infection, and reducing inflammation in the digestive tract. They can also help restore the gut’s natural balance, speeding up recovery.
Probiotics and Immunity: A Stronger Defense System
In addition to supporting gut health, probiotics play an essential role in the immune system. About 70-80% of the body's immune cells are located in the gut, and the gut microbiome has a direct influence on immune function. By improving the composition of gut bacteria, probiotics help to strengthen the immune response and protect the body against infections.
Here’s how probiotics support immune health:
Boosting the Body’s Natural Defense Mechanisms
Probiotics can enhance the body’s ability to recognize and respond to harmful pathogens. Studies show that probiotics may stimulate the production of certain immune cells, such as macrophages and T lymphocytes, which play crucial roles in identifying and attacking invading pathogens.
Certain probiotic strains, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, are believed to produce antimicrobial substances that inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria, fungi, and viruses. Additionally, probiotics help strengthen the intestinal barrier, preventing harmful microorganisms from entering the bloodstream and causing infections.
Reducing Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is linked to a variety of health conditions, including autoimmune diseases, cardiovascular disease, and even cancer. Probiotics can help modulate the immune system and reduce excessive inflammation in the body. They achieve this by influencing the production of cytokines, which are signaling molecules that regulate the immune response.
By balancing the immune response and reducing inflammation, probiotics may help prevent or manage chronic inflammatory conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and rheumatoid arthritis.
Supporting the Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (GALT)
The gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) is a major part of the immune system that resides within the intestines. It is responsible for detecting pathogens and coordinating immune responses. Probiotics are thought to interact with GALT, influencing immune cell activity and promoting a healthy immune balance. This interaction helps protect the body against infections without triggering excessive immune responses that could lead to autoimmune diseases.
Scientific Evidence: Do Probiotics Really Work?
While much of the research on probiotics is promising, it’s important to note that not all probiotics are the same, and their effects can vary based on the strain and dosage used. The benefits of probiotics are often strain-specific, meaning that one strain may be effective for a particular condition, while another may not.
For example, probiotics such as Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and Saccharomyces boulardii have been shown to reduce the risk of antibiotic-associated diarrhea, while other strains may be more effective for conditions like IBS or inflammatory bowel disease.
Additionally, while probiotics can help support the immune system and promote gut health, they are not a cure-all. They should be considered a complementary tool in a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management.
How to Incorporate Probiotics Into Your Diet
There are several ways to include probiotics in your daily routine:
-
Fermented Foods: Incorporate probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut, miso, and kombucha into your diet. These foods contain live cultures that can support the growth of beneficial bacteria in your gut.
-
Probiotic Supplements: If you’re not able to get enough probiotics from food, supplements are a convenient option. Probiotic capsules, tablets, or powders are widely available, but it’s important to choose products with a variety of strains and high potency.
-
Prebiotics: Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that act as food for beneficial gut bacteria. Combining prebiotics with probiotics can further enhance gut health. Foods like bananas, garlic, onions, and whole grains are excellent sources of prebiotics.
-
Consistency is Key: To reap the benefits of probiotics, it’s important to take them consistently. Gut health is a long-term process, and the positive effects of probiotics may take time to manifest.